Quitting smoking and losing weight are two healthy lifestyle choices that can help you avoid senior health risks, but you also need to be physically active and eat a healthy diet. Having a geriatrician, a doctor who specializes in the health issues of aging, on your senior healthcare team may help you begin to live comfortably with any chronic illnesses. You can also seek home care services either for you or your loved one so that someone can help you with everything around the house. Then, you may join the 41 percent of individuals over 65 who report having very good or exceptional health, as per the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Otherwise, you will likely be among the 59%.
Arthritis in Old People
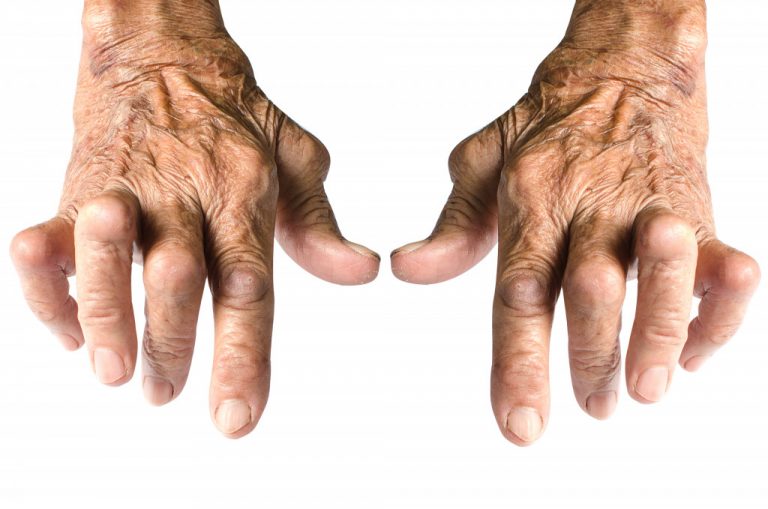
Most people think of arthritis as a disease characterized by painful, inflexible joints. In reality, there are many types of arthritis, each with its own set of symptoms and therapies. The majority of forms of arthritis are chronic, with symptoms persisting for years.
Arthritis may affect joints in almost every area of the body. Some types of arthritis produce visible and palpable changes in your joints, such as pain, swelling, warmth, and redness. Other kinds make less bothersome symptoms but gradually harm your joints.
Arthritis is one of the most prevalent illnesses in the United States. This illness affects millions of adults, including half of all individuals aged 65 and older. The most common types of arthritis in older adults are osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, and gout.
Osteoarthritis
The most prevalent form of arthritis in elderly individuals is osteoarthritis (OA). OA develops when cartilage becomes ragged and wears away. Cartilage is the soft tissue that cushions the bones in a joint. OA tears away all of the cartilage in a joint, leaving bones that rub against one other at its worst. You are most likely to develop OA in your hands, neck, lower back, or major weight-bearing joints like your knees and hips.
OA symptoms may vary from moderate stiffness and pain that comes and goes with movements such as walking, bending, or stooping to severe joint discomfort that persists even when you relax or attempt to sleep. When you haven’t moved your joints in a long, like as after a vehicle ride, OA may cause them to feel stiff. However, when you move the joint, the stiffness goes away. If OA impacts your back, knees, or hips, you may have difficulty moving your joints and, in some cases, incapacity.

Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune illness that affects the joints. In the case of RA, this implies that your body assaults the lining of a joint in the same way that it would if it were attempting to defend you from damage or illness. If you had a splinter in your finger, it would become inflamed—painful, red, and swollen. Your joints get inflamed as a result of RA. This inflammation results in discomfort, edema, and stiffness that last for many hours.
RA may affect almost every joint in the body, including the fingertips, wrist, elbows, shoulders, knees, ankles, feet, legs, and neck. If you have RA in one joint on one side of your body, the identical joint on the other side of your body is likely to have RA as well. RA not only wreaks havoc on joints, but it may also harm organs like the heart, muscles, blood vessels, neurological system, and eyes.
Gout
One of the most excruciating types of arthritis is gout. An attack may start when uric acid crystals develop in connective tissue and joint areas. These deposits cause joint swelling, redness, heat, discomfort, and stiffness.  Gout attacks are often triggered by shrimp, liver, dry beans, lentils, anchovies, or gravy. Alcoholism, being overweight, and certain medicines may all aggravate gout. Some blood pressure medications may potentially raise the likelihood of a gout episode in elderly individuals.
Gout attacks are often triggered by shrimp, liver, dry beans, lentils, anchovies, or gravy. Alcoholism, being overweight, and certain medicines may all aggravate gout. Some blood pressure medications may potentially raise the likelihood of a gout episode in elderly individuals.
Final Thoughts
Each kind of arthritis is treated individually, although there are some standard therapeutic options. Resting, exercising, sticking to a well-balanced diet, and knowing how to keep your joints healthy are essential aspects of managing arthritis. Walking with the proper shoes and a cane can alleviate discomfort in the feet, knees, and hips. You may also discover devices that will assist you in opening jars and bottles or turning the doorknobs in your home more effortlessly. Consult your doctor and other healthcare providers regarding how you can treat arthritis. They will likely encourage treatment and a lifestyle change, but it will help you cope and have a better quality of life.